Security built for critical infrastructure


Compliance overview
Cognite’s Secure Development lifecycle, spanning infrastructure, applications, and operations, are tested and audited by third parties, demonstrating compliance to:
ISO 27001, ISO 9001, SOC 2 Type 2 and CCC+
Cognite supports customers with specific regulatory and industry requirements. Cognite Data Fusion supports customers to meet the following industrial security requirements:
NIST CSF, IEC 62443.2-4, IEC 62443.3-2, IEC 62443.3-3, IEC 62443.4-1, CMMC, FIPs, NERC CIP v.5, GxP
Cognite can provide reports to prospective customers attesting to compliance with the following standards and frameworks:
SOC 2 Type 2 (Security), ISO 27001, ISO 9001
Secure development lifecycle
Cognite’s security engineering team is focused on security features and management controls throughout Cognite Data Fusion’s secure development lifecycle. This team works closely with engineering, solution architects, and implementation teams to ensure security is addressed in design through operation. These security practices are supported by:
Shared responsibility
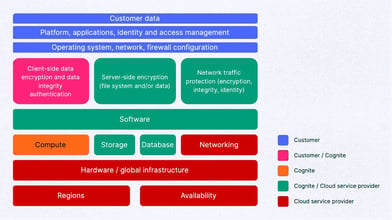
Cognite’s shared security responsibility model relies on collaboration between customers, cloud service providers, and Cognite.
Authentication, access and authorization
Cognite builds secure applications that minimize complexity for users. Cognite Data Fusion leverages customer’s existing identity management platforms to support Zero Trust.
Data security
Data security and privacy are foundational to Cognite Data Fusion. Data is encrypted in transit and at rest, with Cognite authenticating, authorizing, and logging activity. Cognite has robust controls in place to prevent data leakage or intentional/accidental compromise between customers in a multi-tenant environment. Cognite Data Fusion provides:
Resilience
Deployment is continuous and incremental to minimize disruption. Cognite routinely tests business continuity and disaster recovery plans (tabletop and real exercises) that validate scenarios and functionality, including confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Cognite security resilience controls support NIST 800-61 controls such as:

Documentation

White Paper

White Paper

Cognite news

Digitalization community

Blog Post